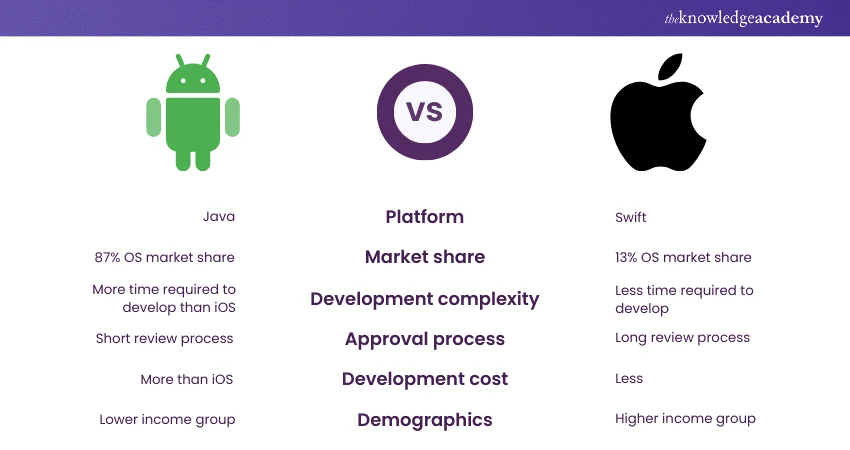
Overview Table
| Aspect | Android | iOS |
|---|---|---|
| Core Philosophy | Open, customizable, device-diverse | Closed, controlled, ecosystem-focused |
| Device Variety | Wide range across brands and prices | Limited to Apple devices |
| User Interface | Highly customizable | Consistent and minimal |
| App Ecosystem | Flexible, broad, customizable | Curated, polished |
| Performance Optimization | Hardware-dependent | Deep hardware–software integration |
| Updates | Brand and model dependent | Direct and long-term updates |
| Security Approach | User-controlled with flexibility | Strict, centralized control |
| Daily Usability | Adaptable to user habits | Predictable and stable |
| Target Users | Power users, budget buyers, tinkerers | Simplicity seekers, ecosystem users |
Introduction
The debate between Android and iOS has shaped the smartphone industry for more than a decade. These two operating systems dominate global mobile usage and represent fundamentally different philosophies about how people should interact with technology. While both platforms aim to simplify daily life, they take distinct paths to achieve that goal. Android emphasizes flexibility, choice, and customization, while Android vs iOS focuses on consistency, stability, and tight integration.
Android vs iOS For daily use, the question is not about which operating system is objectively superior, but which one aligns better with individual habits, expectations, and priorities. Daily use encompasses routine tasks such as communication, browsing, media consumption, productivity, navigation, and personal organization. In these areas, small differences in design philosophy can significantly affect user satisfaction.
This article offers a comprehensive, balanced, and deeply analytical comparison of Android and iOS, examining how each performs in real-world daily usage. It blends narrative insight, technical explanation, and journalistic perspective to help readers understand not just what these platforms offer, but how they feel to use every day.

Core Philosophy and Design Approach
Android’s Open Ecosystem Mindset
Android was designed as an open platform. Its foundation encourages experimentation, customization, and manufacturer-level innovation. This openness allows multiple hardware brands to build devices with unique features, software layers, and price strategies. As a result, Android is less about uniformity and more about adaptability.
This philosophy empowers users who want control over how their device looks, behaves, and integrates with other tools. From changing launchers to installing third-party app stores, Android places fewer restrictions on how the system can be used.
iOS and Controlled Consistency
Android vs iOS operates on a different principle: control enables refinement. Apple tightly manages both hardware and software, ensuring every Android vs iOS in nearly the same way. This results in a highly consistent experience across devices, regardless of price or generation.
By limiting customization and system-level access, Android vs iOS reduces variability. This control allows Apple to optimize performance, security, and user experience with precision. For daily use, this translates to predictability and reduced complexity.
User Interface and Everyday Navigation
Android’s Customizable Interface
Android’s interface is built around user choice. Home screens can be redesigned with widgets, third-party launchers, icon packs, and dynamic layouts. Notifications are interactive and expandable, allowing users to respond, manage tasks, or dismiss alerts efficiently.
Navigation gestures and button layouts can be altered to suit user preferences. This flexibility makes Android feel personal, but it can also feel fragmented depending on the device brand and software version.
iOS and Intuitive Uniformity
Android vs iOS prioritizes simplicity and visual clarity. The interface is designed to be instantly familiar, even for first-time users. Gestures are consistent across apps, animations are smooth, and system elements behave predictably.
Widgets exist but are more structured and limited in placement. Notifications are clean but less interactive compared to Android. For daily use, Android vs iOS reduces decision fatigue by keeping interactions uniform and restrained.
App Ecosystem and Daily Functionality
Android App Freedom
Android supports a broad range of apps with fewer restrictions. Developers have more freedom in app behavior, background processes, and system access. This enables advanced automation tools, file managers, and customization apps that deeply integrate with the operating system.
Daily tasks like downloading files, managing storage, or integrating third-party services feel more flexible. However, this freedom also means app quality can vary significantly.
iOS App Refinement
Android vs iOS apps benefit from strict review guidelines. This results in a generally polished ecosystem where apps are optimized for performance, security, and interface consistency. Developers design specifically for Apple’s hardware, which reduces fragmentation.
For daily use, apps tend to feel smoother and more reliable. However, system restrictions limit what apps can do in the background or how deeply they interact with the operating system.
Performance in Everyday Use
Android Performance Variability
Android performance depends heavily on hardware and manufacturer optimization. On well-optimized devices, daily tasks feel fast and responsive. Multitasking, split-screen usage, and background processing are strengths of the platform.
Lower-end devices may experience inconsistency due to heavier software layers or limited hardware resources. Daily performance can vary widely across the Android ecosystem.
iOS Performance Consistency
Android vs iOS is optimized for a small range of devices. This allows Apple to fine-tune performance at a granular level. Even older iPhones often deliver smooth daily performance thanks to efficient memory management and optimized animations.
App launch times, scrolling, and gesture responsiveness remain consistent. For daily use, Android vs iOS feels stable and predictable regardless of device age.
Multitasking and Productivity
Android’s Productivity Strengths
Android excels in multitasking. Features such as split-screen mode, floating windows, and advanced background processes support productivity-oriented workflows. File management is flexible, making it easier to move documents between apps and storage locations.
Users who rely on email, document editing, and task automation often benefit from Android’s openness. Daily productivity tasks can be handled with fewer system limitations.
iOS Productivity Approach
Android vs iOS emphasizes focused usage rather than multitasking depth. While recent versions have improved multitasking, particularly on larger devices, the system still prioritizes simplicity.
File management exists but remains abstracted from the user. This reduces complexity but can feel restrictive for users who prefer direct control. For daily productivity, Android vs iOS works best when tasks align with Apple’s intended workflows.
Communication and Social Interaction
Messaging and Calls on Android
Android integrates deeply with various messaging platforms. Users can set default apps for calls, messages, and browsing. SMS, third-party messaging apps, and communication tools coexist seamlessly.
Call handling, contact management, and spam filtering can be customized extensively. For daily communication, Android offers flexibility and choice.
iOS Communication Experience
Android vs iOS centralizes communication around its native apps. Messaging, calling, and video chat feel tightly integrated. Contact syncing and call continuity across devices enhance convenience for ecosystem users.
While customization is limited, reliability and simplicity define the daily communication experience on Android vs iOS.
Security and Privacy in Daily Use
Android’s User-Controlled Security
Android provides granular permission controls, allowing users to decide how apps access data. Advanced users can monitor background activity, restrict system access, and customize security behavior.
This control empowers users but also places responsibility on them to manage permissions wisely. Daily security depends partly on user awareness.
iOS and Centralized Privacy
Android vs iOS enforces strict privacy rules at the system level. App permissions are transparent, and background access is tightly regulated. Apple’s approach minimizes user involvement while maximizing baseline protection.
For daily use, this results in fewer privacy decisions but also less flexibility in how apps function.
Updates and Long-Term Usability
Android Update Fragmentation
Android updates depend on device manufacturers. Some brands deliver timely updates, while others lag behind. This affects daily use by influencing access to new features and security patches.
Long-term usability varies widely across devices, making brand choice critical.
Android vs iOS Update Reliability
Apple delivers updates directly to all supported devices simultaneously. This ensures consistent access to new features, security improvements, and performance enhancements.
For daily users, this creates a sense of longevity and trust in long-term device support.
Hardware Integration and Ecosystems
Android Device Diversity
Android supports a vast range of devices and accessories. From budget phones to premium flagships, users can choose hardware that fits their needs. Integration with third-party devices and platforms is flexible.
Daily use benefits from this diversity, especially for users with mixed-device environments.
iOS Ecosystem Strength
Android vs iOS shines within Apple’s ecosystem. Seamless integration with other Apple devices enhances daily convenience. Features like cross-device syncing and continuity improve workflow efficiency.
This ecosystem is powerful but works best when users commit fully to Apple hardware.
Learning Curve and Accessibility
Android Learning Experience
Android’s flexibility can introduce complexity. New users may face a steeper learning curve due to customization options and manufacturer-specific interfaces.
However, accessibility features are extensive, allowing users to tailor the experience to individual needs.
iOS Ease of Use
iOS is widely regarded as intuitive. The learning curve is gentle, making it accessible to users of all ages. Accessibility features are deeply integrated and consistent.
For daily use, iOS minimizes friction and cognitive load.
Reliability and Stability
Android Stability Factors
Stability on Android depends on device quality and software optimization. Well-maintained devices perform reliably, but inconsistencies can arise due to app behavior or system modifications.
Daily reliability improves with careful app management and updates.
iOS Stability Reputation
Android vs iOS prioritizes stability through controlled system access and optimized app behavior. Crashes and slowdowns are less frequent, contributing to a dependable daily experience.
Cost and Value Perception
Android’s Price Flexibility
Android devices exist across all price segments. This accessibility allows users to choose devices that match their budget without sacrificing core functionality.
Daily value perception is strong, especially for budget-conscious users.
iOS Premium Positioning
Android vs iOS devices occupy a higher price bracket. The cost reflects ecosystem integration, long-term support, and consistent performance.
For daily users, value is derived from longevity and reliability rather than upfront affordability.
Which Is Better for Daily Use?
Android for Adaptability
Android suits users who value control, flexibility, and choice. It adapts to varied lifestyles and usage patterns. Daily use feels empowering for those who enjoy customizing their experience.
iOS for Simplicity and Stability
Android vs iOS appeals to users who prioritize ease of use, consistency, and seamless integration. Daily use feels smooth, predictable, and low-maintenance.
Conclusion
Android and Android vs iOS represent two mature, well-developed visions of mobile computing. Neither is inherently better for daily use in all situations. Android excels in flexibility, customization, and affordability, making it ideal for users who want control and variety. iOS excels in stability, simplicity, and ecosystem integration, making it ideal for users who value consistency and long-term reliability.
The better choice ultimately depends on how you use your smartphone every day. If your daily routine involves customization, multitasking, and cross-platform integration, Android offers unmatched freedom. If your routine values seamless performance, intuitive design, and minimal maintenance, Android vs iOS delivers a refined experience.
In daily life, the best operating system is the one that aligns most naturally with your habits, priorities, and expectations.

